Building Your Network in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI): A Step-by-Step Guide
Every reliable cloud deployment starts with a solid network foundation. In OCI, that foundation is the Virtual Cloud Network (VCN)—a private, software-defined network for your compute, databases, and services. This guide explains compartments, public vs private subnets, and a practical setup flow.
1. Tenancy, Compartments, and VCNs
Your tenancy is your company’s root account. Inside it, create compartments—logical containers for isolation, access control, and cost tracking.
DMCloudArchitect (Tenancy) ├─ Production │ ├─ Networking │ ├─ Compute │ └─ Databases └─ Development ├─ Networking ├─ Compute └─ Databases Keep network resources in a dedicated Networking compartment for clean IAM and troubleshooting.
2. What Is a VCN?
A VCN is a private, customizable network in a single region that can span multiple ADs. You define IP ranges (CIDRs), subnets, gateways, routes, and security.
- Example VCN CIDR:
10.0.0.0/16 - Example Subnets:
10.0.1.0/24(public),10.0.2.0/24(private)
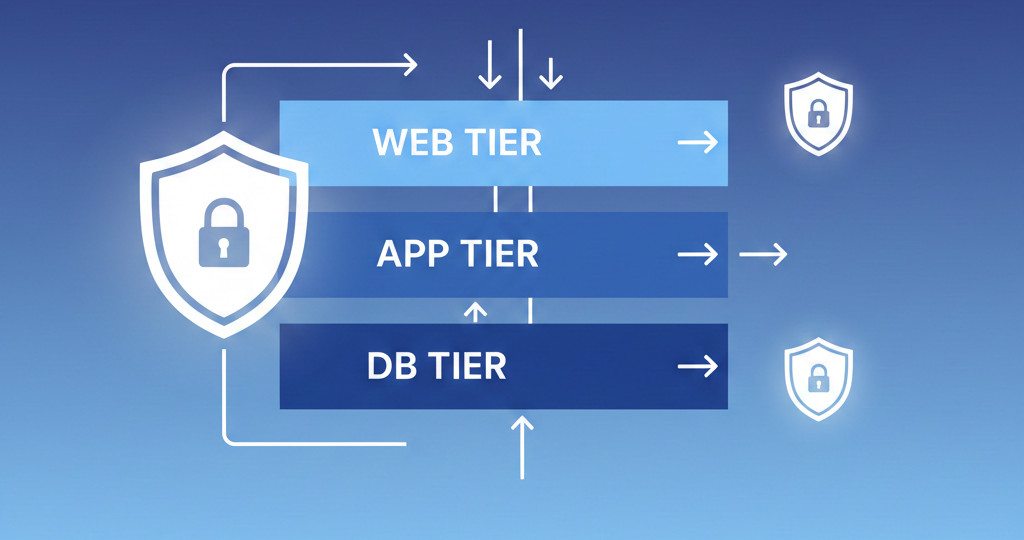
3. Public vs Private Subnets
Public Subnets
- Internet access via an Internet Gateway.
- For web frontends, bastions, public LBs.
- Instances can have public IPs.
Private Subnets
- No direct internet exposure.
- For databases and internal services.
- Outbound only via NAT Gateway for updates.
4. Create a Basic Network (Console)
- Create a Compartment: Identity & Security → Compartments → Create.
- Create a VCN: Networking → Virtual Cloud Networks → Create (Quick setup or Custom). Choose CIDR like
10.0.0.0/16. - Create Subnets:
Public-Subnet 10.0.1.0/24,Private-Subnet 10.0.2.0/24. - Configure Routes: Public →
0.0.0.0/0 → Internet Gateway; Private →0.0.0.0/0 → NAT Gateway. - Security: Use NSGs or Security Lists. Example: allow TCP 22 (SSH) from your IP to public; allow DB port from app subnet only.
5. Key Networking Components
- Internet Gateway: public ingress/egress
- NAT Gateway: private egress only
- Service Gateway: private access to OCI services
- DRG: on-prem/VPN or inter-VCN connectivity
- LPG: local peering same region
- Route Tables: traffic paths per subnet
- NSGs/Security Lists: firewall policies
6. Organizing for Growth
- Plan non-overlapping CIDRs for future peering/VPNs.
- Use tags for owner/cost center.
- Separate prod vs dev in distinct compartments/VCNs.
- Document the IP plan early.
VCN: 10.0.0.0/16 ├─ Public Subnet: 10.0.1.0/24 (Web) └─ Private Subnet: 10.0.2.0/24 (DB)7. Tips for Developers & Small Businesses
- Start with Quick Create; customize later.
- Keep most resources private; expose only what’s needed.
- Automate with Terraform/CLI for repeatability.
- Use Flow Logs and Monitoring for troubleshooting.
8. Summary
Organize with compartments, define a clean VCN, split public/private subnets, and apply least-privilege security. A solid network unlocks secure, scalable deployments for your workloads.