Introduction
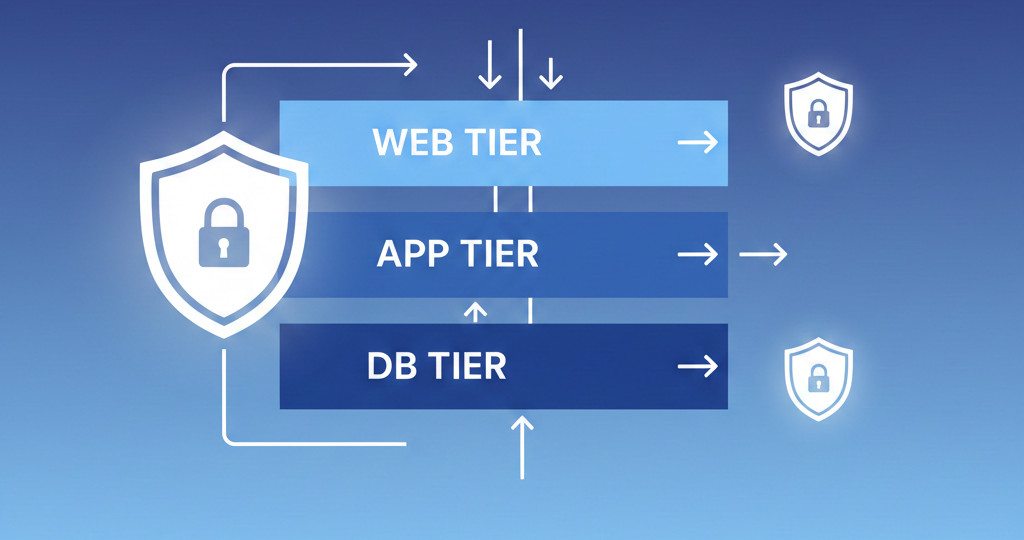
Security in the cloud starts with identity. OCI’s Identity and Access Management (IAM) gives you fine-grained control over who can access what, ensuring the principle of least privilege across users, groups, and resources.
Core Concepts
OCI IAM consists of five main building blocks:
-
Users – individual accounts
-
Groups – collections of users with shared permissions
-
Dynamic Groups – automatic identity for compute instances
-
Policies – written rules that define permissions
-
Compartments – logical containers for isolating resources
Sample Policy Examples
Grant a group full control over a compartment:
Grant read-only access:
Grant a compute instance permission to read Object Storage:
Best Practices
-
Avoid using the root user for daily tasks
-
Create a “Security Admin” group to manage IAM
-
Use compartments for isolation between environments (dev, test, prod)
-
Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for all admin users
-
Audit all IAM activity using Cloud Guard
Conclusion
OCI IAM provides enterprise-grade control with human simplicity. When configured properly, it ensures your environment stays secure, compliant, and well-organized.