1. Introduction
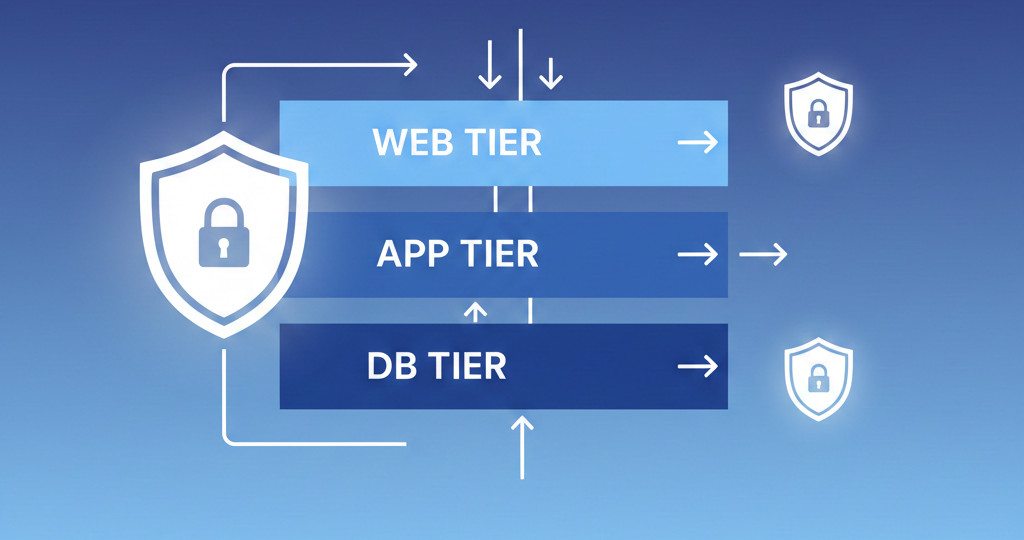
In this guide, we'll design and build a classic three-tier architecture in OCI—web, application, and database layers. This is the setup used by nearly every enterprise workload because it provides scalability, separation of concerns, and strong security boundaries.
2. What Problem This Solves
Most OCI tenants run everything in one subnet, causing:
-
No segmentation
-
Broad security rules
-
Exposed databases
-
Hard-to-scale infrastructure
A multi-tier model fixes all of this.
3. Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1 — Create 3 Subnets
Step 2 — Create NSGs
-
web-nsg→ allow 80/443 -
app-nsg→ allow port 8080 from web -
db-nsg→ allow port 3306/1521 from app
Step 3 — Configure Gateways
-
Internet Gateway → web tier
-
NAT Gateway → app & DB
-
Service Gateway → DB for backups
Step 4 — Deploy Instances
-
Web servers in public subnet
-
App servers in private subnet
-
DB (MySQL HeatWave or ATP) in DB subnet
Step 5 — Route Tables
Web Subnet:
App Subnet:
DB Subnet:
4. Architecture Diagram
5. Best Practices
-
Always use NSGs over security lists
-
Limit communication only between tiers
-
Push static objects to Object Storage or CDN
-
Offload SSL at the load balancer
-
Enable autoscaling for web/app tiers
6. Troubleshooting
| Issue | Cause | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| App can’t talk to DB | NSG misconfigured | Add correct source NSG |
| DB can't back up | No service gateway | Add SGW and route |
| Web not accessible | LB health check failing | Check port and firewall |
7. Summary
This architecture is the gold standard for scalable, secure cloud deployments. OCI gives you all tools needed to build it cleanly and efficiently.
👉 Download your free guide:
7 OCI Networking Mistakes to Avoid
https://dmcloudarchitect.com/c/7_oci_mistakes_to_avoid.html