1. Introduction
In this guide, I’ll show you how to secure your Oracle Cloud network with the same approach I use in production customer environments. OCI offers enterprise-grade networking features—if configured properly.
Security starts with the network. And in OCI, that means controlling access with VCNs, subnets, security lists, NSGs, IAM, gateways, and monitoring.
2. What Problem This Solves
Most tenants are exposed because:
-
0.0.0.0/0 is allowed everywhere
-
Unnecessary public IPs
-
No segmentation between app and DB layers
-
No egress control
-
No flow logs or monitoring enabled
-
IAM policies too broad
This guide eliminates those risks.
3. Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1 — Lock Down SSH
Never allow:
Instead use:
-
your office IP
-
VPN
-
Bastion service
Step 2 — Replace Security Lists with NSGs
Network Security Groups allow instance-level control, not subnet-level.
Create NSG:
Add ingress rule:
Step 3 — Use Private Subnets Everywhere
Public subnet = only for:
-
Load balancers
-
Bastion host (if not using OCI Bastion)
App and DB should ALWAYS be private.
Step 4 — Enable VCN Flow Logs
Use for:
-
blocked traffic troubleshooting
-
security audits
Step 5 — Configure IAM the Right Way
Never assign Administrators group to developers.
Follow least privilege:
-
network admins → manage virtual-network-family
-
db admins → manage database-family
-
devs → manage instance-family
Example policy:
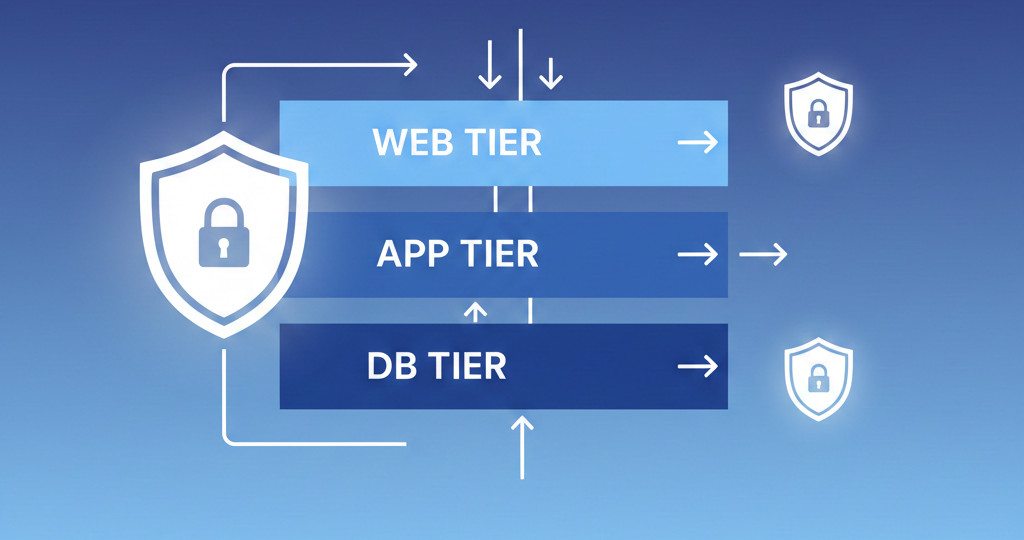
4. Architecture Diagram
5. Best Practices
-
Use NSGs per tier: web, app, db
-
Use Vault for secrets, not environment variables
-
Disable unused protocols (ICMP, UDP)
-
Use IPSec VPN or FastConnect for enterprise workloads
-
Add alarms (port scans, unusual traffic)
6. Common Errors / Troubleshooting
| Problem | Cause | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| App can't reach DB | NSG blocking | Add DB port in NSG |
| Slow traffic | Wrong MTU | Set MTU 1500 or test jumbo frames |
| Outbound internet blocked | Missing NAT route | Fix route table |
| Policy denied | Wrong IAM | Update group policy |
7. Summary
Security is not a feature—it’s a discipline. By applying OCI’s VCN, NSG, IAM, and logging tools correctly, you build a hardened cloud environment that minimizes attack surface and maximizes reliability.
👉 Download your free guide:
7 OCI Networking Mistakes to Avoid
https://dmcloudarchitect.com/c/7_oci_mistakes_to_avoid.html